How To Configure Host Names in Windows 10 and 11 and manage hostnames is a fundamental aspect of networking in any operating system. In Windows 10 and 11, a hostname identifies a device on a network, allowing it to be addressed and accessed by other devices. Correctly configuring your hostname is crucial for network functionality, name resolution, and various network services. This article will guide you through the process of configuring hostnames in Windows 10 and 11 using a simple yet effective method involving Notepad.
Understanding Windows Host Names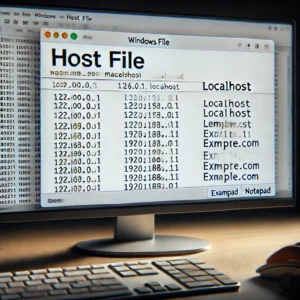
A hostname acts as a label for your computer on a network, much like a street address identifies a house. It allows other devices to locate and communicate with your system. Without a properly configured hostname, network browsing, file sharing, and other essential network operations can be disrupted or completely unavailable. Therefore, understanding the role and importance of hostnames is the first step towards effective network management.
Windows uses a combination of the hostname and the primary DNS suffix to create the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). The FQDN provides a complete and unambiguous identifier for the computer within a specific domain or network. For example, if your hostname is “mycomputer” and your primary DNS suffix is “example.com,” your FQDN would be “mycomputer.example.com.” This FQDN is what distinguishes your computer from other devices with potentially similar hostnames on different networks.
It’s important to choose a descriptive and relevant hostname that adheres to network naming conventions. Avoid using spaces or special characters in your hostname. Sticking to alphanumeric characters and hyphens is generally recommended for compatibility and consistency across different systems and network protocols. Using a consistent naming scheme also simplifies network administration and troubleshooting.
Configuring the Hostname with Notepad and Examples
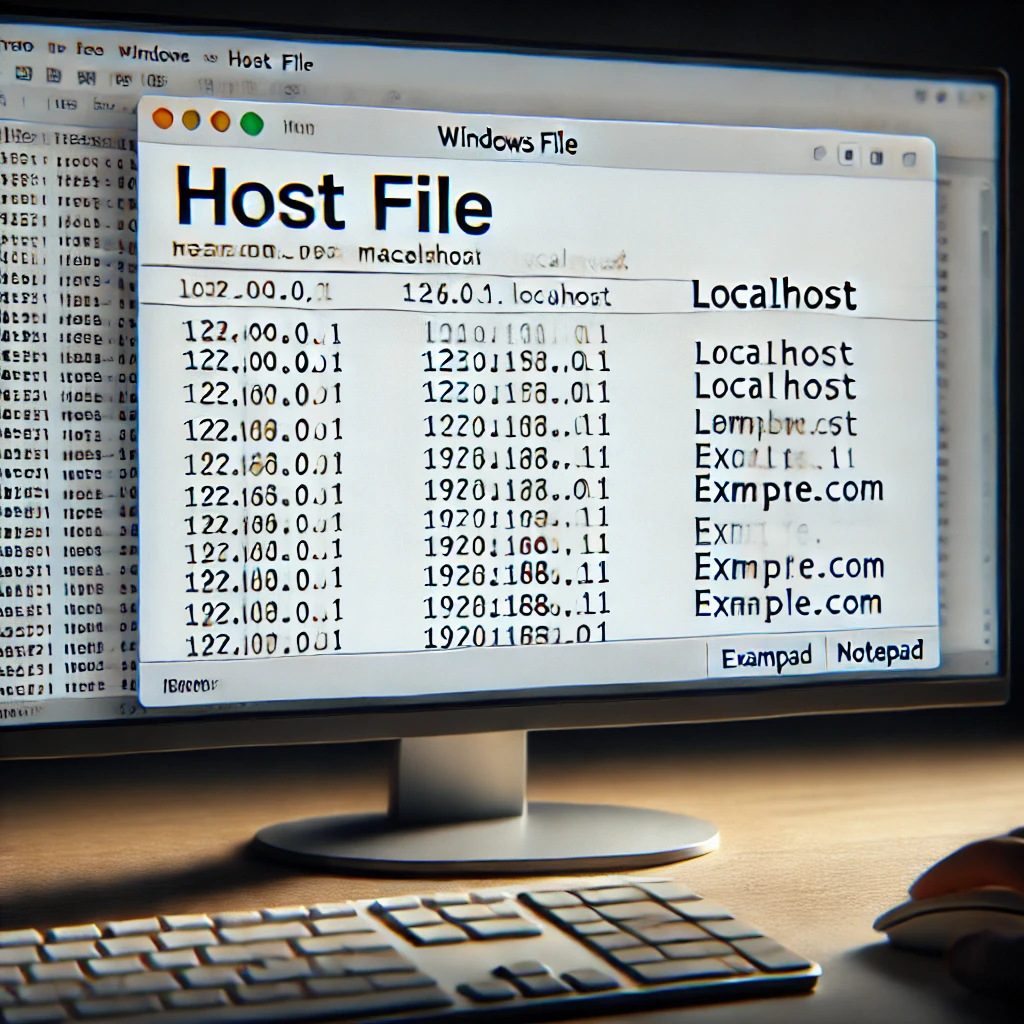
One straightforward method to configure the hostname involves modifying the “hosts” file using Notepad. This file, located at C:Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts, acts as a local DNS resolver, mapping hostnames to IP addresses. While typically used for testing or overriding DNS settings, it can also be employed to set the hostname. However, it’s important to note that changes made to the hosts file primarily affect the local machine.
To modify the hostname, open Notepad as an administrator. Navigate to C:Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts. Add a line at the end of the file, following this format: 127.0.0.1 new_hostname. Replace new_hostname with your desired hostname. For example, if you want to set your hostname to “workstation1,” the line would be 127.0.0.1 workstation1. This entry associates the loopback IP address (127.0.0.1) with your new hostname.
After saving the changes, you will likely need to restart your computer for the new hostname to take effect. Once restarted, you can verify the change by opening the command prompt and typing hostname. The command should return your newly configured hostname. While this method is relatively simple, it’s essential to remember that it primarily affects local name resolution. For changes to propagate across the network, configuring the hostname through system settings is generally recommended.
Example 1: Setting hostname to “desktopPC”
Add the following line to the hosts file: 127.0.0.1 desktopPC
Example 2: Setting hostname to “server01”
Add the following line to the hosts file: 127.0.0.1 server01
Example 3: Setting hostname to “laptop-home”
Add the following line to the hosts file: 127.0.0.1 laptop-home
Configuring hostnames in Windows 10 and 11 is a relatively simple process that plays a vital role in network communication. Understanding the importance of hostnames and utilizing the Notepad method described above can provide a quick and effective way to manage your device’s network identity. Remember to choose descriptive hostnames and adhere to naming conventions for optimal network management. While the hosts file method is useful, consider using the system settings for network-wide propagation of hostname changes.
More How To Guides can be found here